Your pages aren’t getting indexed. Rankings feel stuck. Traffic isn’t growing.
The problem might not be your content—it could be your sitemap.
Many website owners ask the same question: Is an XML or HTML sitemap better for SEO? The answer isn’t as simple as choosing one and moving on. Each sitemap serves a different purpose, and using the wrong one—or ignoring one entirely—can quietly hurt your search visibility.
In this guide, you’ll learn the clear difference between XML and HTML sitemaps, how search engines actually use them, and which one helps SEO the most. You’ll also understand when you should use one, when you should use both, and how the right choice can improve indexing, crawl efficiency, and user experience.
By the end, you’ll know exactly which sitemap fits your website’s SEO goals—and how to avoid common mistakes that hold rankings back.

Ask an SEO: Is An XML Or HTML Sitemap Better For SEO?
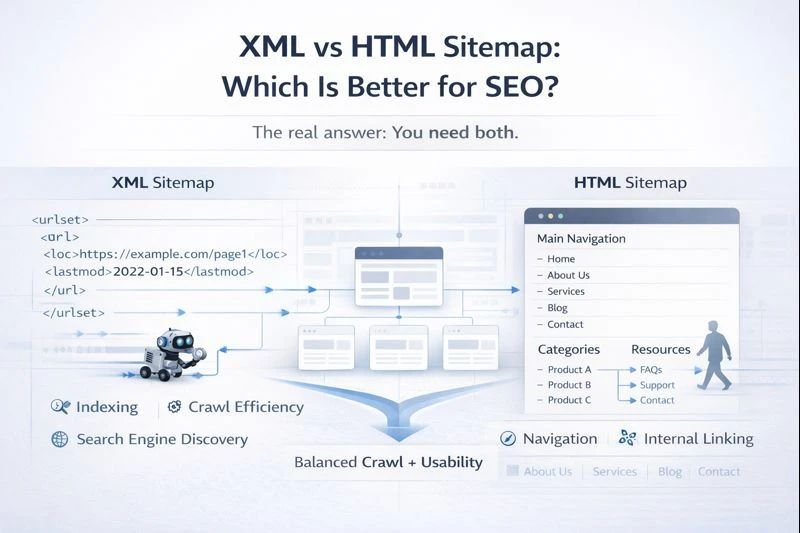
What Is An XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file made for search engines, not users. It lists your important pages in a clean format so Google and other search engines can find, crawl, and index them faster. Think of it as a roadmap that tells search engines, “These pages matter. Please don’t miss them.”
What Is The XML Sitemap Used For?
The main goal of an XML sitemap is better indexing. It helps search engines discover new pages, updated content, and pages that may not be well linked internally. This is especially useful for large websites, new sites, or pages buried deep in the structure.
XML sitemaps help search engines:
- Find pages faster
- Understand site structure
- Notice content updates
- Crawl efficiently without wasting budget
Best Practices For XML Sitemaps
To get real SEO value, follow these basics:
- Include only important, indexable URLs
- Keep it updated automatically
- Submit it in Google Search Console
- Use one sitemap per 50,000 URLs
- Avoid redirect, noindex, or error pages
Things To Be Aware Of With XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap doesn’t guarantee rankings. It only helps discovery. If your content is weak or blocked by technical issues, a sitemap won’t fix that. Also, adding every URL can confuse search engines instead of helping them.
Also read: How We Use XML Sitemaps to Improve Indexing, Crawl Efficiency, and SEO Growth
What Is An HTML Sitemap?
An HTML sitemap is a page made for users. It lists important pages in a simple, clickable format so visitors can easily find what they need. Unlike an XML sitemap, it looks like a normal web page and helps both users and search engines understand your site layout.

What Is An HTML Sitemap Used For?
The main purpose of an HTML sitemap is better navigation. It helps users who feel lost and gives search engines extra internal links to crawl. While it’s not a direct ranking factor, it supports SEO by improving user experience and internal linking.
An HTML sitemap helps by:
- Improving site navigation
- Reducing bounce rates
- Passing link equity to deeper pages
- Helping crawlers discover important URLs
Best Practices For HTML Sitemaps
To get SEO value, keep it clean and useful:
- Include only key pages, not everything
- Organize links by category
- Keep anchor text clear and natural
- Place it in the footer for easy access
Things To Be Aware Of With HTML Sitemaps
HTML sitemaps shouldn’t replace good menus or internal links. If it’s overloaded with links, it can confuse users and dilute SEO value. Also, it won’t help much if your site already has strong navigation.
Example: Large eCommerce sites often use HTML sitemaps to help users quickly reach category pages, improving engagement and crawl depth.
Subscribe for Daily Search Insights
Want simple SEO tips that actually work? Subscribe Digital Arka for daily search insights and stay ahead of Google updates, ranking changes, and real-world SEO strategies.
Which Is Better To Use For SEO?
The short answer: neither is “better” on its own. XML and HTML sitemaps serve different SEO roles. One helps search engines crawl smarter. The other helps users navigate better. When used together, they support stronger indexing, cleaner site structure, and better overall SEO performance.
When To Use The XML Sitemap
Use an XML sitemap when your goal is faster and more reliable indexing. It’s essential if your website is large, new, or frequently updated. Search engines rely on it to understand which pages matter most.
An XML sitemap is best if you:
- Have hundreds or thousands of pages
- Publish new or updated content often
- Have pages that are deep in your site
- Want better crawl efficiency
- Are managing a new or growing website
This sitemap talks directly to search engines. It doesn’t improve user experience, but it makes sure your pages are found and crawled.
When To Use The HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap works best when user experience is the priority. It supports SEO by improving internal linking and helping visitors find important pages easily.
Use an HTML sitemap if you:
- Have complex navigation
- Want to improve internal link flow
- See users dropping off due to poor navigation
- Run content-heavy or eCommerce websites
HTML sitemaps also help search engines discover pages through real, clickable links, which adds an extra layer of crawl support.


